Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Galvanized Steel Sheet is a common material in construction and industry. Its durability and corrosion resistance make it a popular choice. This material undergoes a galvanization process, coating it with zinc. This coating protects the steel underneath from rust and degradation.
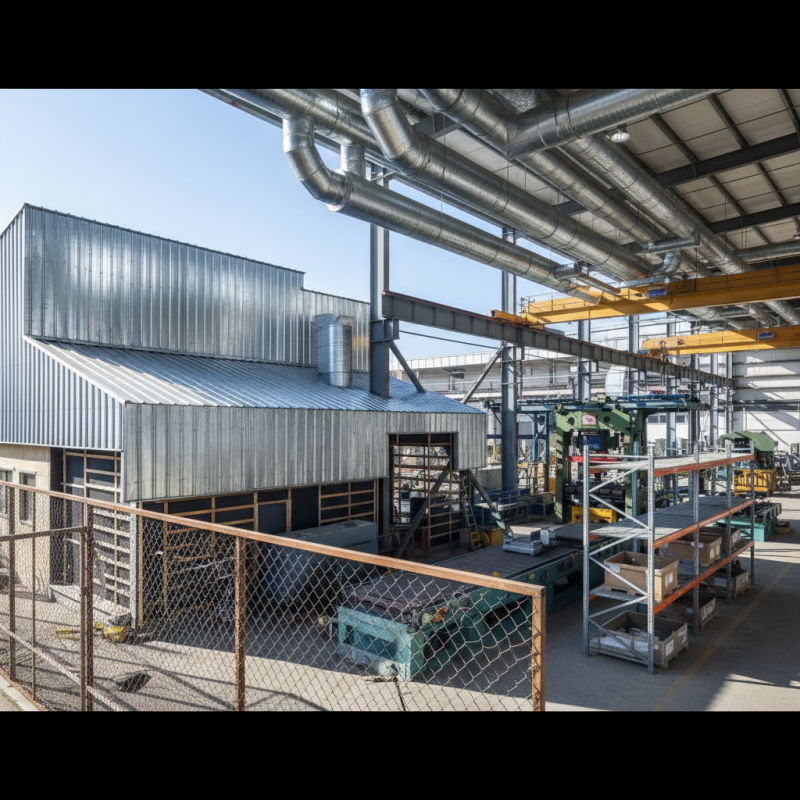
The uses of Galvanized Steel Sheet are diverse. It is often found in roofing systems, fences, and HVAC ducts. In industrial settings, it supports machinery components and storage solutions. Its versatility is remarkable. Yet, the weight of galvanized steel can be a consideration for some projects. Budget constraints also affect its usage choices.
Overall, Galvanized Steel Sheet plays a significant role in various applications. While it offers numerous benefits, it is essential to weigh those against potential challenges. Understanding both sides can lead to smarter decisions in construction and industry.

Galvanized steel sheets are increasingly vital in modern construction. They offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for various applications. Reports indicate that the global demand for galvanized steel is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 5% from 2023 to 2028. This growth highlights the material's importance in building sustainable structures.
In construction, galvanized steel sheets are prevalent for roofing, siding, and flooring. Their durability can significantly reduce maintenance costs. A study shows that structures using galvanized steel often have a lifespan of over 50 years, compared to traditional materials. This longevity is crucial in a market focused on sustainability.
However, challenges remain. Some builders hesitate to use galvanized sheets due to initial costs. The perception of higher upfront expenses may deter investments. Additionally, not all galvanized steel sheets are equal. Variations in coating thickness can lead to performance discrepancies. This inconsistency requires careful selection based on specific construction needs. While galvanized steel has numerous advantages, careful planning and evaluation are necessary.

Galvanized steel sheets are increasingly popular in construction. Their unique properties make them ideal for various applications. One key benefit is their resistance to corrosion. This is vital in outdoor environments or humid conditions. Structures made with galvanized steel last longer, requiring less maintenance over time.
Another advantage is their strength-to-weight ratio. They provide substantial support without excessive weight. This makes them perfect for roofing and cladding. Architects appreciate their versatility. They can be easily fabricated into different shapes and sizes. However, it's important to note that not all projects may benefit equally from galvanization.
Cost considerations can also be a challenge. While initial expenses may be higher, the longevity of the material can offset these costs. Using galvanized steel can lead to reduced material waste. Still, one must evaluate if it aligns with the project's overall budget. Additionally, not all galvanized products are created equal; some may have varying levels of zinc coating. Careful selection is crucial.
Galvanized steel sheets are widely used in various industrial applications. They offer significant benefits, including corrosion resistance and durability. According to industry reports, the global demand for galvanized steel is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5% from 2021 to 2026. This growth is driven by several sectors, including construction, automotive, and appliance manufacturing.
In the construction industry, galvanized steel sheets are commonly used for roofing and siding. Their resistance to rust makes them ideal for exposed environments. They provide an extra layer of protection, ensuring longevity. HVAC systems also use galvanized steel due to its ability to withstand harsh conditions. However, the performance can vary based on the thickness of the coating applied.
Tips: When selecting galvanized steel sheets, consider the environment they will be exposed to. Different applications require different coatings. Regular inspections are also crucial to identify any signs of wear or damage. Don't skip this step; it can save costs in the long run.
In industrial settings, galvanized sheets are used in making storage tanks and pipes. Their strength and resilience make them a popular choice. However, it's essential to reflect on the overall sustainability of using galvanized materials. While they provide short-term benefits, the long-term impact on the environment deserves attention. Explore more sustainable options when possible.
| Application | Industry | Advantages | Typical Thickness Range (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Frameworks | Construction | Durability, corrosion resistance | 1.0 - 3.0 |
| Roofing Sheets | Construction | Weather resistance, lightweight | 0.5 - 1.0 |
| Automotive Components | Automotive | Cost-effective, strength | 0.5 - 2.0 |
| Fencing and Gates | Agriculture | Longevity, low maintenance | 0.8 - 1.5 |
| Electrical Enclosures | Electronics | Protection from environmental factors | 0.6 - 1.2 |
| Storage Tanks | Industrial | Corrosion resistance, structural integrity | 1.5 - 4.0 |
When comparing galvanized and non-galvanized steel sheets, durability is a key factor. Galvanized steel is coated with zinc, which enhances its resistance to corrosion. This protective layer can last for over 30 years in many environments. Non-galvanized steel, however, starts to rust within months when exposed to moisture. Industrial applications frequently favor galvanized steel for this reason.
Another critical aspect is cost-effectiveness. Galvanized steel sheets typically have a higher upfront cost than non-galvanized sheets. However, the long-term savings in maintenance and replacement make them more economical over time. According to a report by the American Galvanizers Association, maintenance costs for galvanized steel can be reduced by up to 70%.
Tip: When choosing materials, consider the environment. Coastal areas require more robust solutions due to increased humidity and salt exposure.
In terms of aesthetics, galvanized steel sheets can look slightly less refined compared to their non-galvanized counterparts. This might not be a concern for functional applications, but it can be important in architectural settings. Some people find the appearance unappealing. It’s essential to balance function with design in such cases.
Tip: Always test materials in your specific application before making a large purchase. This ensures compatibility and performance.
Galvanized steel sheet has become an essential material in construction projects. Its sustainability is notable. According to a report by the World Steel Association, steel is the most recycled material globally. In fact, about 90% of steel used today is recycled. This significantly lowers the environmental impact associated with its production and use.
Moreover, galvanized steel offers longevity unmatched by many alternatives. The estimated lifespan of galvanized steel structures is over 50 years. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements and repairs, especially in harsh environments. A study from the U.S. Department of Energy shows that the embodied energy of galvanized steel is lower than that of other materials. This means it requires less energy to produce and process.
However, challenges do exist. Some construction professionals overlook local regulations regarding galvanized materials. Also, corrosion can occur if not installed properly. Awareness and training in best practices are crucial. The industry must address these gaps to fully utilize the potential of galvanized steel in sustainable construction.