Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
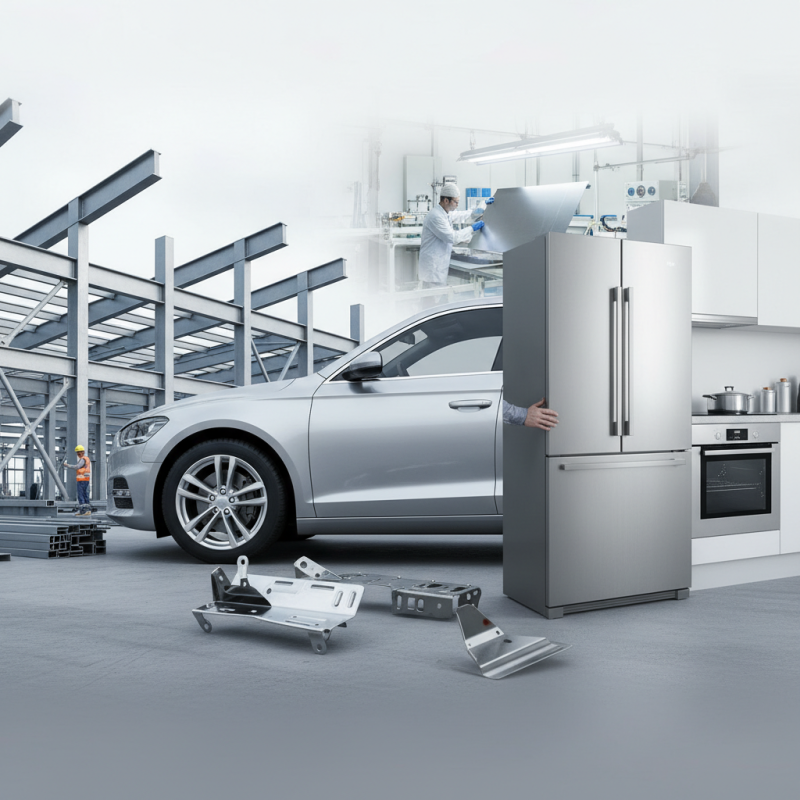
Steel Sheet is a vital material in various industries. Its versatility is evident in construction, automotive, and appliances. Made from rolled steel, it comes in various thicknesses and grades. This adaptability makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers.
In construction, Steel Sheet forms structural components like beams and frames. It also acts as a protective shell in buildings. The automotive industry uses it for body panels and parts, ensuring durability and strength. Appliances, such as refrigerators and ovens, often feature Steel Sheet for a sleek finish and reliable structure.
Despite its many uses, some challenges exist. Steel Sheet can corrode without proper treatment. It's essential to consider environmental factors that affect its longevity. Continued innovation in coating techniques aims to enhance its durability. Understanding these aspects encourages more thoughtful use of Steel Sheet across different sectors.

Steel sheet is a versatile material widely used in various industries. It is created through a process of steelmaking and can come in various thicknesses. The thickness typically ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. This material is known for its durability and resistance to corrosion. It provides structural support in many applications.
In construction, steel sheets are often used for roofing and siding. They offer strength against harsh weather conditions. In the automotive industry, they are essential for manufacturing car bodies. The ability to shape and mold steel sheet makes it ideal for complex designs. It can be cut, welded, and formed into different shapes, creating endless possibilities.
However, working with steel sheets does present challenges. Cutting and shaping require precision. This can lead to waste if not executed carefully. Also, proper safety measures are essential when handling steel. Despite these drawbacks, the benefits of steel sheet in engineering and design are significant. Its role in modern infrastructure cannot be underestimated.

Steel sheet is a key material in various industries, known for its versatility and strength. The composition of steel sheets typically includes iron, carbon, and other alloying elements. This combination offers different mechanical properties. For instance, low carbon steel sheets contain about 0.05-0.25% carbon, while high carbon types may have between 0.30-2.0%. This range affects everything from ductility to hardness.
When it comes to types, there are several. Hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets are the most common. Hot-rolled sheets are produced by rolling steel at high temperatures, making them easier to shape. Cold-rolled sheets, on the other hand, are processed at room temperature, resulting in a smoother finish and tighter tolerances. According to a recent industry report, hot-rolled steel sheets account for over 50% of global production. However, cold-rolled sheets are gaining traction due to demand for precise applications.
Despite their advantages, there are challenges. Quality control can be a concern, as variations in thickness and composition affect performance. Additionally, sustainability remains an ongoing discussion. The steel industry is working to reduce carbon emissions and innovate cleaner processes. As the need for efficient and durable materials grows, understanding steel sheet composition and types is crucial.
Steel sheets are created through various manufacturing processes that can significantly affect their properties and uses. One common method is hot rolling. In this process, large steel slabs are heated and passed through rollers to create thin sheets. This method produces sheets that are strong but may have surface imperfections. These imperfections can impact their aesthetic quality but are often corrected later in the process.
Cold rolling is another technique that helps refine steel sheets. Here, sheets are processed at room temperature to increase their strength through strain hardening. The sheets become thinner and smoother, making them ideal for applications where precision is key. However, the process can lead to increased brittleness, which may pose challenges in certain applications. Striking a balance between strength and malleability is crucial.
Other methods, such as electrogalvanizing, are used to enhance corrosion resistance. This involves applying a zinc coating to the steel sheets. While effective, it may introduce complications with adhesion in some applications. Manufacturers must carefully consider the chosen process to suit specific needs without compromising quality. Each method has unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective use of steel sheets in various industries.
Steel sheets play a crucial role across various industries. The automotive sector extensively utilizes them for manufacturing body panels due to their lightweight and high strength. In fact, a recent report by the Steel Institute indicates that up to 30% of a vehicle's weight can be attributed to steel components.
Construction is another significant area where steel sheets are indispensable. They are used in structural frameworks, roofs, and walls. According to industry data, steel sheets account for roughly 45% of the material used in modern construction. Their durability ensures longevity, even in adverse weather conditions.
Tips: When selecting steel sheets, consider thickness and corrosion resistance. Both factors greatly affect performance. Regular maintenance can extend their lifespan.
The appliance industry is also a notable user. Refrigerators and ovens often feature steel sheets in their construction. However, there are challenges. Improper welding or cutting can weaken the structure. This aspect demands careful attention to detail during production to avoid costly errors.
Steel sheets are essential in various construction and fabrication processes. Their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for supporting structures. According to the American Iron and Steel Institute, steel provides a robust option for buildings, ensuring safety and durability.
Using steel sheets offers several advantages. They are versatile and can be easily shaped and sized for specific projects. This adaptability reduces waste during production. Additionally, steel sheets are resistant to corrosion when properly treated, which extends their lifespan significantly. A report from the Steel Institute reveals that using galvanized steel can enhance longevity by up to 50% compared to non-treated alternatives.
Tips: Always consider the specific requirements of your project. Choosing the right thickness can impact both cost and structural integrity. Don't overlook the importance of surface treatment. Prioritize quality to avoid potential issues down the line. Proper research before selecting materials can lead to more efficient and effective outcomes.
| Dimension | Material Type | Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Length (mm) | Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Sheet | Mild Steel | 2.0 | 1000 | 2000 | Construction, Manufacturing | Cost-effective, Easy to work with |
| Corrosion-resistant Sheet | Stainless Steel | 3.0 | 1200 | 2500 | Food industry, Chemical processing | Durable, High resistance to corrosion |
| Galvanized Sheet | Galvanized Steel | 1.5 | 1500 | 3000 | Roofing, Siding | Rust-resistant, Versatile |
| High-strength Sheet | High-strength Low-alloy Steel | 5.0 | 2000 | 6000 | Heavy machinery, Structural applications | Lightweight, High strength |